The time taken to program and tune FA installations before production can begin is increasing with the growing demand for small-batch production. At the same time, the number of experts that can perform such procedures is shrinking. Mitsubishi has therefore combined its drive-control expertise with AIST’s Bayesian optimisation application technology to produce an AI technology that reduces the time needed to set up FA equipment and systems.
For example, the developers claim that they can reduce the time needed to set up servo system positioning parameters to just one day, compared to around a week that it could take experts to set up such systems by hand.
When using servo systems for positioning control, it is necessary to establish optimal parameters to achieve the desired speed and acceleration for each position and distance. Vibration and other characteristics can vary, depending on the target position and travel distance, and it can be difficult to adjust the large numbers of parameters required.
Mitsubishi says that its new technology can optimise up to 720 parameters – a number that even experts would have difficulty adjusting. As well as saving commissioning time, the system is also claimed to reduce positioning times up by to 20%.
One area where Mitsubishi and AIST have applied their technology is robotics. They claim that they can cut programming times by up to 66%, especially when having to deal with anomalies such as errors in grasping or alignment.
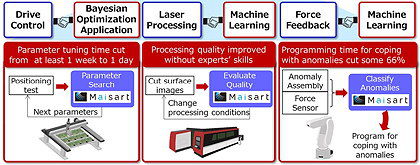
Mitsubishi says that its jointly developed AI technology will cut set-up times in a range of automation applications
The new technology learns to classify such anomalies by combining Mitsubishi’s robotic force-feedback control technology with AIST’s machine-learning expertise. It eliminates the need to develop anomaly-classifying algorithms, which conventionally must be created separately for each system.
Another area of application is in laser-based cutting of sheet metal. Here, the technology is being used to determine the processing quality automatically without needing experts. Various factors can affect the processing quality of these machines, such as debris on the lens that focuses the laser beam, or the condition of the workpiece surface. These can result in the cut surface being scratched or discoloured, reducing its quality. Conventionally, experts need to check the surface and make adjustments to improve quality.
An automatic quality-evaluation technology that combines Mitsubishi’s laser-processing know-how with AIST's machine-learning technology for image recognition, is now said to be achieving a similar level of performance to experts. The procedure also allows the operators to change machine settings based on the automatic evaluations, and to improve processing quality, without consulting experts.

